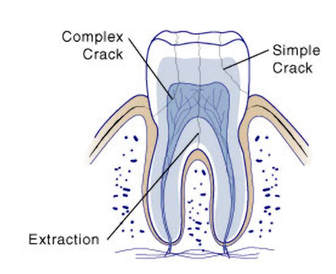
 Like bones, our teeth are very resilient and strong. With proper dental care and regular dental check-ups with your pediatric dentist, you can keep them healthy and strong. But no matter how meticulous you are, accidents happen. And sadly, it could lead to a cracked tooth. What is Cracked Tooth Syndrome? Cracked tooth syndrome happens when a tooth has a tiny crack that’s can only be seen under X-rays or is beneath the gums and difficult to see. Accidents, biting hard food such as ice or candy or teeth grinding can result in a cracked tooth. Cracked tooth syndrome most often appear on the molars because they do most of the chewing. Symptoms of a cracked tooth may be noticeable or not, but it is important to visit your dentist right away. The dentist can check the molar and see how serious the crack is. Signs and Symptoms of a Cracked Tooth Most often, cracked tooth syndrome can be asymptomatic, which means that it does not have any signs and symptoms. Thin, hairline fractures that don’t reach the sensitive part of the teeth often left unnoticed until it reaches the point when the tooth breaks in half. Later on, these tiny fractures may promote the growth of bacteria, which can lead to tooth decay. However, there are a number of common symptoms to watch out for. Pain may be hard to localize and often comes and go. You may be very sensitive to cold or hot drinks. In some cases, you can feel a sharp edge of a tooth using your tongue. If you notice any of these, visit your dentist immediately for repair. How to Fix Cracked Tooth Syndrome The spreading of cracks can be slowed down or even stopped by seeking early intervention. To detect tiny cracks on the teeth, a small, high-intensity light is applied to illuminate the teeth. Through this, any tiny, unseen fractures can easily be found using this technique. If detected at the earliest stage, the chip or crack can be repaired without the risk of losing the tooth. The treatment approach for Cracked Tooth Syndrome will depend on the position and severity of the cracks. Simple crack treatment involves removal of the weakened cusp and replacement of a crown or a large filling. The new crown or filling will protect the tooth and prevent any crack from spreading. A complex crack procedure is needed if the crack has reached the nerve or has already caused inflammation. At this stage, a root canal therapy may be necessary. If a simple crack is ignored and left untreated, it may become a complex crack over time. The dental nerve inside may die and infection may take place. At this point, a root canal may be required or sometimes, the removal of the tooth.  Baby teeth must be extracted to ensure incoming permanent tooth to emerge without problems such as misalignment and crowding. Oftentimes, milk teeth are naturally lost or pulled out from force which is common among children. If your child’s tooth has been removed, the aftercare needed extends past the dental office. Proper dental care is as important as the procedure to ensure that your child’s gums heal quickly and prevent any infection. Below are some proper care tips after tooth extraction from Mint Kids Dentistry. Right After the Tooth Extraction Avoid swishing and using a straw. Within 24 hours post-extraction, the freshly exposed tooth socket will be very sensitive. To prevent dislodging healing blood clot, be sure not to introduce a straw to your child within this period. When sipping, the suction made can remove the clot, which could lead to further bleeding. In addition, swishing any liquids must not be encouraged as it can loosen the clots. Eat soft food. Within 24 hours after extraction, give only soft foods that don’t need too much chewing. The gum area will be very sensitive that chewing solid foods can be painful and uncomfortable. Soft foods that you can give include soup, yogurt, mashed potatoes, pancakes, eggs and apple sauce are perfect within 24 hours of pulled tooth. In addition, avoid serving too hot or too cold food as the gums are very sensitive to extreme temperatures. As the affected area heals, you’ll be able to add more solids into their diet but it is suggested to continue giving soft foods for a week. Take pain reliever as prescribed. You can give your child pain medications to reduce pain and discomfort. Tips 2 to 7 Days After Pulled Tooth Use ice packs. Your child may experience swelling a couple of days after tooth extraction. To ease the pain and swelling, you may apply ice pack over a swollen cheek ever 2 to 3 hours or as necessary. Wrap ice in thin towel or cloth and apply it over swollen area for 15 minutes. Have a saltwater rinse. After 24 hours, it is now safe to rinse exposed socket with warm saltwater to clean the area. Combine 8 ounces of warm water with a teaspoon of salt and have it swished in their mouth for a few seconds before spitting out. Saltwater helps clean the mouth and ease the pain on the sensitive area. Hands off. Your child should not touch the exposed area to keep it clean. Tell your child to avoid picking or touching the extraction area as this practice introduces germs that can delay the healing process and may lead to infection. Brush your teeth. Although your child’s mouth will be sensitive after several days post-extraction, they must continue brushing their teeth for 2 minutes, twice a day. However, they must do it much gentler than the usual and avoid brushing the exposed socket to prevent bleeding. Flossing should also be continued. If the pain or swelling does not subside after three days post-extraction or if the pain worsens after several days, contact your pediatric dentist immediately to rule out an infection.  Most parents think that sugar is the worst enemy of the teeth. Acid-producing bacteria devour on sugar and produce damaging acids that attack the tooth enamel. But did you know that sodium can also affect oral health? How Salt Causes Tooth Decay You might be wondering how salt can cause damage to your dental health. While salt itself doesn’t damage tooth enamel, simple carbohydrates and sodium usually come together, particularly on processed foods. Just like sugar, bacteria inside the mouth feast on the simple carbs and produce acids when you consume food containing carbohydrates. When acids remain in the mouth for longer period, the more time it damages the enamel. Many people, including children, consume more salt than needed. · Fast food such as pizza and pasta often contain lots of salt. · Many processed foods have salt in them. · Packet foods such as corn chips, potato chips and even crackers contain excessive salt. · Canned foods often have salt. Although most of these food are low in sugar, the starches they contain are broken down my mouth enzymes into simple sugar. Simple sugar produce the same damaging effects as sugar would. Other Hidden Dangers of Excessive Salt Intakes Sodium may be directly damage the teeth, leading to cavities, but a sodium-rich diet can actually weaken the teeth. Like the bones, your teeth depend on calcium for strength and structure. A diet high in sodium has been found to reduce the level of calcium in the body. Since sodium increases urine output, many minerals, including calcium and potassium get excreted through urine. This leads to osteoporosis and even tooth loss. How Much Salt Does My Child Need? The daily suggested intake of salt depends on the child’s age: · For 1 to 3 years old, 2 grams of salt per day · For 4 to 6 years old, 3 grams · For 7 to 10 years old, 5 grams · For 11 and up – 6 grams No matter what your diet would be, it is important that you maintain your kid’s daily oral hygiene, including dental checkups and cleanings.  Eating disorders such as binge eating, bulimia and anorexia nervosa are not uncommon among teens. Obsession over their weight affects millions of adolescents, particularly girls. A study has found that about 36% of adolescent girls think they are overweight. Over 90% of cases of eating disorders are girls. Teen boys, while they also experience body image concerns, often strive for a perfect body by doing excessive exercise. What is Eating Disorder? The most popular forms of eating disorders include bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa, and binge eating disorders. Eating disorders are psychological disorders involving extreme disturbances on a person's eating behavior. For instance, a teenager with bulimia suffers from frequent binge eating followed by the use of laxatives or vomiting to get rid of the food. An anorexic person refuses to maintain a normal body while a binge eater has uncontrolled overeating. How Eating Disorders Affect Dental Health Here’s a list of dental complications brought about by eating disorders: 1. Due to inadequate nutrition, the gums and other tissues inside the mouth may be damaged easily. A teen may suffer chronic dry mouth or swelling of the salivary gland. 2. Self-starvation, as in the case of anorexia nervosa, usually lead to nutritional deficiency or malnutrition. Nutrients necessary for healthy teeth and gums include iron, calcium, and B-vitamins. Insufficient intake of these essential nutrients can lead to gum disease and tooth decay. 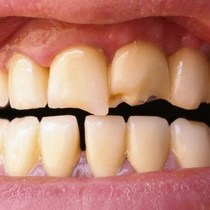 3. Frequent vomiting leads to harsh gastric acid coating the teeth repeatedly. Vomit is highly toxic and damaging to your teeth and oral tissues as it contains stomach acid. When this happens over and over again, the enamel may be lost and the teeth may change its shape, color, and translucence. The teeth may become brittle, weak and highly sensitive. Drinking hot or cold beverages may be very uncomfortable. The edges of the teeth usually thin out or break easily. Sometimes, the pulp may be exposed, causing infection or pulp death. 4. Purging can cause redness, irritation, and wounds inside the mouth, specifically on the soft palate or the upper surface of the mouth. When the soft palate is already damaged, this is already a warning sign among dental professionals that the eating disorder is getting worse, as this part rarely gets harmed unless it is done intentionally. Soft palate scratches appear from using fingers to induce vomiting. 5. Frequent purging can lead to enlargement of the salivary glands. This can cause pain and discomfort. How to Manage Oral Health Complications from Eating Disorders In order to maintain oral health, the patient must follow meticulous oral health care such as tooth brushing, flossing, and frequent communication by the pediatric dentist. While curbing the purging behavior, a person must immediately rinse their mouth with water only after purging due to the high acid content of the oral cavity. Brushing must be halted for one hour to prevent scrubbing the acids into the enamel. Dry mouth or xerostomia may occur due to vomiting and this can lead to tooth decay. Moisturize your mouth with water or other suggest products by your dentist to help keep decay at bay. 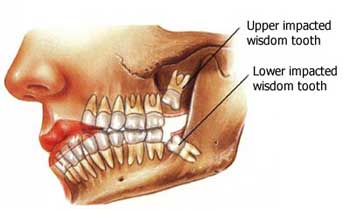 Your child’s mouth undergoes many different changes throughout his/her lifetime. Among the biggest milestone often takes place between the age of 17 and 21 when the third molars erupt. Traditionally, these teeth are called ‘wisdom teeth’ as they emerge at a later age. When they surface at a proper position, wisdom teeth can help you masticate. While it’s normal to feel slight pain or discomfort when your wisdom teeth surface, experiencing intense pain prompts immediate dental check-up. What’s the problem? The appearance of wisdom teeth often leads to problems when there's not enough space for them. When they are misaligned, they may position in a wrong angle, either away from the next molar, inward or outward. They may also become impacted or trapped under the gums or in the jaw. When your wisdom teeth erupt, your pediatric dentist will check the following signs: · When the wisdom teeth are in the wrong position, it allows food to easily get trapped, promoting the growth of acid-producing bacteria that cause a cavity. · Wisdom teeth in the wrong position make flossing a bit difficult between the wisdom teeth and the adjacent molars. · Wisdom teeth that partially erupted can permit the entry of bacteria inside the gums, which may cause an infection. This leads to swelling, stiffness, and pain of the jaw. · Impacted or trapped wisdom teeth inside the gums may damage adjacent teeth or causing crowding of the teeth. · Impacted wisdom teeth can create a cyst, which could damage the dental root of neighboring teeth. When to Remove Your Wisdom TeethGenerally, a wisdom tooth must be removed if it is causing the following symptoms or conditions in the mouth: · Tumors · Cyst · Infection · Pain · Tooth decay · Gum disease · Damage to adjacent teeth Your dentist may advise removing your wisdom teeth as part of a dental treatment such as braces. Before removing your wisdom teeth, your dentist will recommend taking an X-ray and together, you can talk about the best treatment course. When wisdom teeth are not causing any discomforts or changes in the mouth, you still have to keep on monitoring it for possible problems later. Make sure you floss your wisdom teeth, brush it thoroughly and visit your dentist regularly. Source: https://www.mouthhealthy.org/en/az-topics/w/wisdom-teeth  Vitamins and minerals are very important nutrients for your child’s development, both physically and mentally. But did you know they are also vital for his/her dental health? All parts of the body are interconnected, including the teeth and gums. Even a slight deficiency can result to a lasting effect on your child’s oral health. When they are still young, the teeth and gums are still developing and aren’t completely mature, which stresses the necessity to ensure that their food intake is well-balanced with vitamins and minerals. This is primarily the reason why sufficient intake of different vitamins and minerals are necessary to develop their oral health. As a pediatric dentist, below are the list of top nutrients necessary to maintain healthy gums and teeth. Calcium. Calcium is not only important for strong bones, it is also needed for healthy, strong teeth. This mineral supports the development of the teeth, while making them even stronger once they emerged. Since calcium is delivered in different parts of the body, the teeth will be supplied with enough calcium they need, including the jaw that supports it. Providing the proper amount of calcium will help prevent complications such as weakened teeth. Ensure the child eats lots of leafy greens, dairy, sardines, salmon and broccoli to get plenty of calcium. Fluoride. Known to fight cavities, this mineral can prevent further development of tooth decay and support strong healthy enamel, which gives the teeth protection to fight decay-causing bacteria. You can use fluoride dental products, however, many tap waters are now infused fluoride. Vitamin A. This vitamin not supports clear vision and immune boost, it is also necessary for healthy gums. Vitamin A promotes the flow of saliva in the mouth to prevent dryness, promote healing and maintain a healthy environment for the oral cavity. Vitamin A can be sourced in your diet, particularly fish, carrots and dark leafy vegetables. Vitamin D. This essential nutrient plays a major role in the development of bones and teeth as it facilitates the absorption of calcium. Your child must have plenty of Vitamin D to efficiently utilize calcium. Vitamin D can be sourced from sun exposure, fish oils and dairy. Iron. This mineral is necessary in the development of teeth, including the production of red blood cells. A deficiency in iron can cause a wide range of health complication, so make sure your little one eats beans, spinach and red meat. Don’t Miss Their Dental Check-up Your children’s dental health should not completely rely on their dietary intake alone. They must receive regular dental care from their pediatric dentist to monitor any development of carries and properly guide the development of their teeth for a beautiful, perfect smile that can last a lifetime. Puberty is the stage that brings many changes to boys and girls. Puberty in girls usually begin at around 10 to 11 whiles boys are a bit late at 11 to 12. In general, this stage often takes 5 to 6 years, in which children’s reproductive organs and sexual characteristics emerge to maturity. Hormone levels rise, voice changes, bodies and muscles develops, sexual attraction starts and an overall increase in consciousness on self-image and appearance reveals. Along with this general changes, their oral health can also be affected. How Hormone Changes Affect Their Dental Health Hormonal changes during puberty often affects girls and as such, parents should give oral care utmost concern. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone trigger changes in the girls’ bodies. Such sex hormones during puberty stage can cause a number of dental issues including puberty gingivitis, characterized by bleeding and swelling of gums. The onset of menstruation causes an increase of hormones that encourage the growth of oral bacteria. In fact, many girls and even boys during puberty experience symptoms of gum sensitivity and gingival bleeding. Some adult women still experience menstruation gingivitis before their menstruation start. Menstruation gingivitis symptoms include swollen, tender, red gums and mouth sores. Improper oral cancer can worsen these symptoms. Increase in certain hormones can also increase microbial growth, which is the reason why cavities and bad breath are quite common among adolescents. Other Issues on Oral Health As children grows and permanent teeth starts to erupt, they may experience changes in the appearance of their mouth, including the shape of their bite. By the time puberty sets in, most of the adult teeth already surfaced. This is the time when certain orthodontic treatments usually begin. One of the most important concerns for children with braces is the need to maintain proper oral care carefully. Due to the extra attachments on the teeth, there are many corners for food bits to stick to, causing dental carries. Proper tooth brushing and having regular dental visit for professional cleaning are very important to prevent the development of carries. Tooth staining is very common among teens. This is due to changes in diet and consumption of dark soda and tea. How to Manage the Impact of Puberty on Oral Health During puberty stage, many adolescents face many struggles, primarily on their emotional and social aspects. Peer pressure, increased self-consciousness to self-image and identity crisis can affect a child’s focus on proper dental care. Good oral care can make a positive impact on an adolescent’s self-image. Parents should reinforce healthy dental practices through regular brushing and flossing and having proper nutrition. The puberty stage is often the time when a young person faces many changes in his/her life. This is also a great time to practice good dental care habits that they will follow for the rest of their life. |
AuthorMint Kids Dentistry Archives
July 2021
Categories |
Location |
|
Sitemap
|
Forms
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed